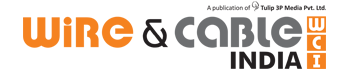The electrical utilities companies in the country are increasingly using optical ground wires (OPGW) to create a reliable communication backhaul to provide unceasing data transmission.
 History
History

OPGW is one of the most reliable fiber optic medium for the telecom service providers, ISPs, Cable TVs, or other organisations who are involved in the transmission of one or more form of voice, data, video, text, messages, conferencing and telemetering kind of things. This provides seamless and robust connectivity (99.999%) expectation of users today. In year 1977, OPGW was patented by BICC UK. Installation became widespread in the year 1980.In 2000, around 60,000km OPGW was installed worldwide. .
Specification (Standards)
OPGW is manufactured as per IEEE Std.1138-2009 and the hardware standard for the installation of the OPGW is IEEE Std.1591.1-2012.
Fiber Standards
Fiber has a core of 8-10 micrometer; and after cladding, it becomes 250 +/- 5 micrometer. Both are generally glass, predominately silica (SiO2). Acrylic, Plastic or composite coating is done for fiber protection during manufacturing, handling and operation. The different standards depending upon the quality of fiber and their usages are G.652, G.652.D, G.653, G.654, G.655, G.656, G.657.A1&A2, etc.
 OPGW Construction
OPGW Construction
Many constructions are available in OPGW, but two are the most common, i.e. steel tube and aluminium tube design. The number of fiber varies from 6-144 in count. Fiber may be in the loose tube or directly in the steel tube. The tube is filled with the thyrotrophic jelly to provide comfort to Fiber as well as to make it water resistant. A few construction details picture is given below to visualise OPGW very easily and clearly.
Utilities are Aggressive
The requirement of bandwidth is increasing like anything. Utilities use a technology called PLCC, which has a limitation to 4.8 kbps and even digital PLCC has maximum capacity of 128 kbps and is not free from EMI (Electromagnetic Interference). Now, the concept of smart grid is impelling utilities to have a communication system based on fiber optic backhaul.
Utilities are implementing the communication system based on fiber optic backhaul in different ways. MSETCL (MAHATRANSCO) has formed a joint venture company with Sterlite Technologies Limited and is in the process of installing 3,500km (approx.) of OPGW cable, of which 2,200km has already been installed so far. The biggest central utility company PGCIL has installed 38,000km (approx.) and is in the process of installing another 25,000km (approx.) in the next three years. Similarly, other utilities such as APTRANSCO (Transmission Corporation of Andhra Pradesh), GETCO (Gujarat Energy Transmission Corporation), TANTRANSCO (Tamilnadu Electricity Transmission Corporation), and KSEB (Kerala State Electricity Board) are also installing OPGW. MPTRANSCO has identified around 17,000km more for its entire network. The utilities in the eastern part of the country are also planning for OPGW installation for the accurate, efficient, and speedy communication.
Tests on OPGW

Electrical Tests: Fault current, lighting performance, etc.
Mechanical Tests: SAG tension of OPGW provided by the NESC (National Electricity Safety Code)
Optical tests: Fiber continuity: fiber break or no break; Attenuation: signal diminishing in total reel and also in db/km; Fiber length: measured by OTDR. Index of refraction is to be provided by the manufacturer.
Environmental Tests: OPGW has to withstand the natural elements like corrosion, wind, fog, ice fall, and others. So, proper test are done to make it fit for the use.
Cable Characteristics Tests: Creep test; stress-strain test; strain margin; ultimate tensile strength (UTS); and DC resistance.
Installation Tests: Sheave, crush, bend, and twist
In service Tests: Aeolian vibration, galloping, short circuit, lighting arc, water ingress, seepage of flooding compound, temperature cycle, salt spray (corrosion), etc.
Accessories for OPGW Installation
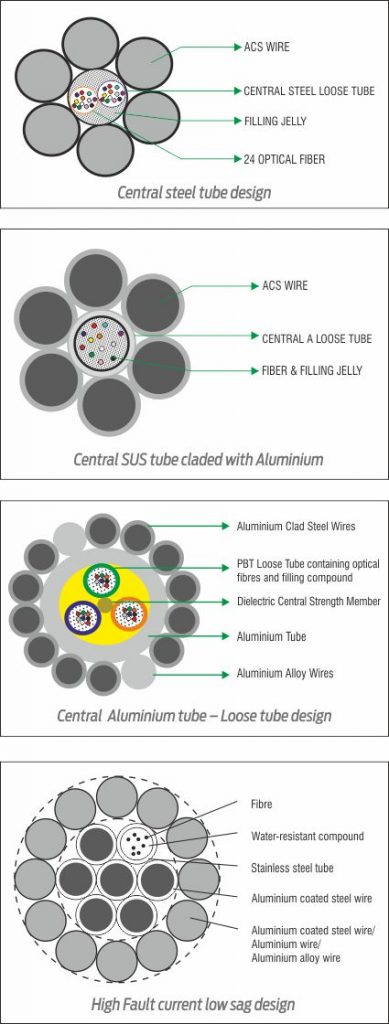
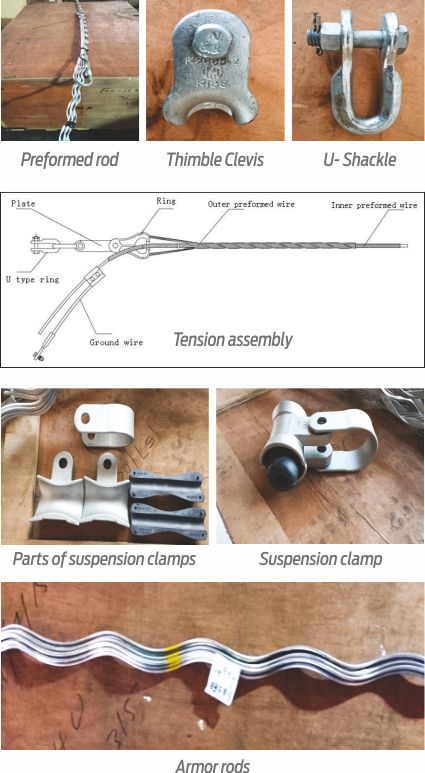
The figures given below shall be self sufficient to depict the accessories used in installation of OPGW cables. Normally, there are two types of towers, viz. tension tower and suspension tower; and accordingly, there are two kinds of the assembly.
 Manufacture in India
Manufacture in India
Sterlite Technologies Ltd. (India), ZTT (China), LS Cable (Korea) and Tiahan (Korea) are the few in OPGW business in the country.
Conclusion
Utility companies have their own ROW for existing transmission line, which they can utilize for their own communication benefits and extra revenue by leasing the spare fiber as well. The rate of IRU is quite good, and that too for long duration, in the range of Rs. 15,000- 25,000 per Fiber km. It will also facilitate the telecom service providers, ISPs and cable operators, struggling for fiber laying (as it is the toughest task for them). The coverage of the signal in the interiors is still a billion dollar question and utilities can bridge this gap to great extent. Another is the employment scope – big team is required in installation with special skill set. There is big scope for the manufacturers as well as for contractors to make good business.