Fire or shock incidents may occur due to electrical faults. In the case of wire or cable, the properties of the insulating materials are critical to controlling physical performance, electrical integrity and fire response. Ascertaining flammability characteristics and other performance characteristics are therefore vital in safety certification of wire and cable. UL LLC (UL) has developed many safety standards and certification programmes for wire and cable products. There are more than 70 wire and cable product categories that are evaluated by UL, such as appliance wiring material, thermoplastic-insulated wire, thermoset-insulated wire, photovoltaic wire, communications cables and flexible cords. This feature article focuses on some of the wire and cable categories, various test methods and the safety requirements for wire and cable products evaluated in accordance with the UL standards.
Introduction
Electrical short circuit could be one of the reasons for fire disasters and the flame propagation along the wire or cable could be attributed to the poor flame-retardant properties of the polymeric materials used in the wire and cable products. Safe wire and cable products are a necessity to mitigate these risks. Compliance of wire and cable products with established standard requirements for flammability and other properties is critical in this regard. UL LLC (UL) has certification programmes based on these standards for more than 70 wire and cable product categories. Flammability, physical properties and electrical properties are the key parameters by which the safety performance of these products is being evaluated. Wire and cable for particular environments or specialty applications may also be evaluated for optional ratings such as oil resistance, gasoline resistance and sunlight resistance.
Appliance Wiring Material
Appliance Wiring Material (AWM) is a wire or cable mainly used in appliances and similar equipment, identified in UL’s online certifications directory () with the category code AVLV2. This type of wire is a component for use in UL certified products as factory-installed wiring either within the overall enclosure of appliances and other equipment (internal wiring) or as external interconnecting cable for appliances (external wiring). The standard used to evaluate these products is ANSI/UL758, Standard for Safety for Appliance Wiring Material. These products are designated by style numbers – such as 1007. Each AWM style has unique specifications that are described on a corresponding style page. For example, Style 1007 is a PVC insulated wire with temperature and voltage ratings of 80°C and 300V respectively.
Methodologies used to evaluate these products include physical properties, conductor corrosion test, deformation test, flexibility test, heat shock test, cold bend test, crush resistance test, dielectric voltage withstand tests, horizontal flame test (for internal wiring) and cable flame test (for external use cables).
Building Wire
Thermoplastic-Insulated Wire and Cable and Thermoset-Insulated Wire and Cable are listed by UL under category codes ZLGR and ZKST respectively. These are common types of wire and cable used for light and power in permanent installations within buildings. These wires and cables are for installation in accordance with the National Electrical Code (NECTM), ANSI/NFPA 70, including Article 310. Thermoplastic-Insulated Wire and Cable are identified by type designations such as TW, THW, THHW and THW-2; Thermoset-Insulated Wire and Cable are identified by type designations such as XHH, XHHW and XHHW-2. The UL standards covering these products are ANSI/UL83, Standard for Safety for Thermoplastic-Insulated Wires and Cables and ANSI/UL44, Standard for Safety for Thermoset-Insulated Wires and Cables.
The methodologies used for evaluating these wires and cables include physical properties, cold bend test, heat shock test, deformation test, flexibility test, dielectric withstand test, short-term insulation resistance test, long-term insulation resistance test, capacitance test and relative permittivity and vertical flame tests.

Flame Tests
Flame tests provide critical information about wire and cable safety. The insulation may be defeated by exposure to flame and may serve to propagate flame. Figure 1 illustrates the type of damage that can occur when wires and cables are exposed to flame sources.
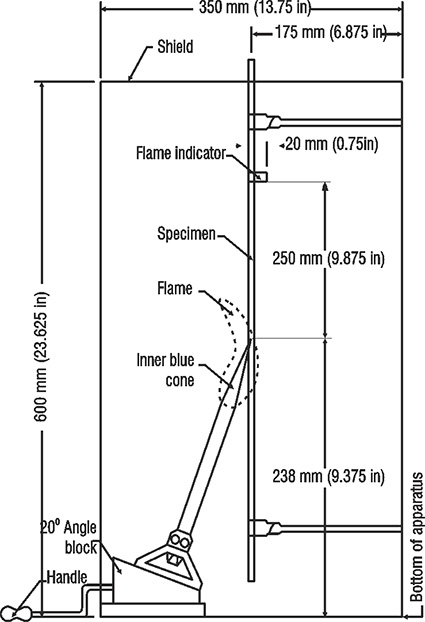
Flame tests are categorised as small-scale flame tests such as horizontal flame test, cable flame test, VW-1, FT1 and FT2 and large scale flame tests such as vertical-tray flame test and FT4 flame test. The flame test methods are intended to evaluate the resistance of the wire and cable insulation to conveying flame along its length and to combustible materials in its vicinity. Different parameters, such as length of char, cotton ignition, indicator flag and flame propagation height, serve as criteria for determining compliance of the flame tests. For instance, in the VW-1 flame test, a flame indicator is placed on the test specimen at a defined location, the specimen is vertically oriented and cotton is placed on the floor of the test chamber. A test flame is applied to the specimen for five 15-second applications. There shall be no ignition of the cotton, the specimen shall not continue to flame longer than 60 seconds after each flame application and not more than 25 per cent of the flame indicator shall be consumed. Refer to Figure 2.

Determination of Temperature Rating
The temperature rating of a wire or cable is important to appropriately match the product to its installation environment and end use requirements. If wires and cables are exposed to over-temperature conditions, the insulation may be defeated and lead to a risk of fire or electric shock. Refer to Figure 3.
The physical properties test is one of the assessments generally conducted for evaluating the temperature rating of a wire or cable. Accelerated aging is performed to assess the potential degradation of the insulation. Tensile strength and elongation of the insulation and jacket materials in a wire or cable are assessed before and after air oven aging for a specific time and temperature. Aging and physical properties requirements for different materials vary. For instance, a PVC material with a temperature rating of 105°C evaluated in accordance with UL758 is subjected to 7 days aging in an air oven at 136°C. PVC should have a minimum tensile strength value of 1500 psi and a minimum elongation of 100 per cent for the un-aged specimens. After oven-aging, the specimens should retain a minimum of 70 per cent for tensile strength and a minimum of 65 per cent for elongation.
Physical Testing
Physical testing of wires and cables provides important information about the integrity of the insulation. The cable may be subjected to a similar environment in the actual service life wherein the insulation and jacket becomes more susceptible to mechanical damage, such as cracking upon bending, causing exposure of conductor and thereby increasing the risk of fire or electric shock.
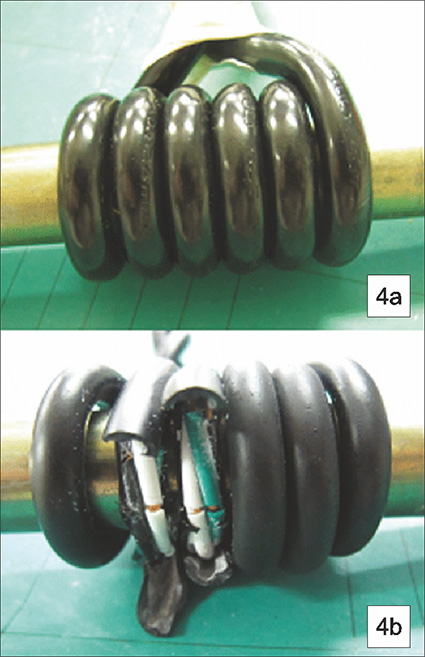
The following example can be considered to understand this. Figure 4 depicts a sample subjected to cold bend test in which a finished cable has been conditioned in a cold chamber for four hours at -10°C. Figure 4a shows the sample before the cold conditioning, and Figure 4b shows the condition after cold conditioning.
Manufacturing Surveillance
UL uses a periodic surveillance programme to provide an increased level of assurance that the products continue to comply with the applicable requirements after the initial certification. As a part of UL LLC’s follow-up service programme, field representatives periodically visit the factory and select samples of the most recent production of the products for test and examination. This level of continued assessment provides confidence that the materials and manufacturing methods in use over the life of the product continue to demonstrate critical safety characteristics.
Summary
Potential hazards associated with wires and cables may be mitigated by appropriate assessments of the products. UL LLC has developed many standards and certification programmes for wire and cable products. Compliance of these products with the standard requirements is critical in the safety certification. UL requirements for Appliance Wiring Material, Thermoplastic-Insulated Wire and Thermoset-Insulated Wire have been developed to address key safety issues, including tests for flammability, temperature rating and cold bending. Periodic surveillance, such as UL LLC’s follow-up service programme, provides confidence in continued compliance of certified products and promotes integrity of the UL mark.
This article has been written by
Mr. V.V. Ray, UL India
(e-mail: V.V.Ray@ul.com)