Thanks to digitization, manufacturing is gradually becoming more productive and flexible. Digitalization is slowly and steadily transforming the way we manufacture products. Referred to as “Industry 4.0” in Europe, the “Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)” in the United States, or just “smart manufacturing”, this transformation represents the fourth revolution that has occurred in manufacturing. The first industrial revolution was all about mechanization through water and steam power; the second industrial revolution was about mass production and assembly lines using electricity; the third industrial revolution was about the adoption of computers and automation; and the fourth industrial revolution is about enhancing the use of computers and automation with smart and autonomous systems fueled by data and machine learning. In other words, Industry 4.0 optimizes the computerization of Industry 3.0.
Introduction of computers in Industry 3.0 proved to be disruptive mainly because a completely new technology had been added to various processes. In Industry 4.0, computers are connecting and communicating with one another to make decisions without human involvement. Cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things and the Internet of Systems are being combined to make Industry 4.0 possible and the smart factory a reality. Smart machines are getting smarter as they get access to more data; and with the support of these machines, factories are becoming more productive and efficient and less wasteful.
What’s Industry 4.0 all about?
The new digital industrial technology or Industry 4.0 enables manufacturers to gather and analyze data across machines, which inevitably entails more efficient, more flexible and faster processes for the production of higher quality goods at reduced costs. Technology experts say that this manufacturing revolution will not only increase productivity and change economics, but also foster industrial growth and modify workforce’s profile. They claim that these changes in manufacturing would ultimately change the competitiveness of companies and regions. Advanced digital technology is already in use in manufacturing; but combined with Industry 4.0, it will transform production in an unbelievable way. This combination will enhance efficiencies and make a big change in traditional production relationships among producers, suppliers and customers. It will also change the relationship between human and machine.
Building blocks of Industry 4.0
The vision of the industrial production of the future, Industry 4.0 is powered by nine technology advances. Many of these advances are already used in manufacturing; but with Industry 4.0, they will transform production – isolated optimized cells will come together as a fully integrated, automated and optimized production flow.
Let us look at the nine technologies that are considered as the building blocks of Industry 4.0:
- Big data and analytics
- Automated robots
- Simulation
- Horizontal and vertical system integration
- The Industrial Internet of Things
- Cyber security
- The cloud
- Additive manufacturing
- Augmented reality
 Big Data and Analytics: In the manufacturing world, analytics based on large data has emerged only recently. It optimizes production quality, saves energy and improves equipment service. In the Industry 4.0 scenario, the collection and comprehensive evaluation of data from various sources will become standard to support real-time decision-making.
Big Data and Analytics: In the manufacturing world, analytics based on large data has emerged only recently. It optimizes production quality, saves energy and improves equipment service. In the Industry 4.0 scenario, the collection and comprehensive evaluation of data from various sources will become standard to support real-time decision-making.
 Automated Robots: Robots are becoming more and more autonomous, cooperative and flexible, and it will not be long before they start interacting with one another and work safely with humans and learn from them. These automated robots will cost less and have a wider range of capabilities than those used in manufacturing today.
Automated Robots: Robots are becoming more and more autonomous, cooperative and flexible, and it will not be long before they start interacting with one another and work safely with humans and learn from them. These automated robots will cost less and have a wider range of capabilities than those used in manufacturing today.
 Horizontal and Vertical System Integration: With Industry 4.0, companies, departments, functions and capabilities will become much more cohesive, as cross-company, universal data-integration networks evolve and enable automated value chains.
Horizontal and Vertical System Integration: With Industry 4.0, companies, departments, functions and capabilities will become much more cohesive, as cross-company, universal data-integration networks evolve and enable automated value chains.
 The Industrial Internet of Things: With the Industrial Internet of Things, many devices will be enriched with embedded computing and connected using standard techno-logies, thereby allowing field devices to communicate and interact both with one another and with more centralized controllers as required. In addition, it decentralizes analytics and decision-making, enabling real-time responses.
The Industrial Internet of Things: With the Industrial Internet of Things, many devices will be enriched with embedded computing and connected using standard techno-logies, thereby allowing field devices to communicate and interact both with one another and with more centralized controllers as required. In addition, it decentralizes analytics and decision-making, enabling real-time responses.
 Cyber Security: Because increased connectivity and use of standard communications come with Industry 4.0, the need to protect critical industrial systems and manufacturing lines from cyber-security threats will become stronger. Hence, secure, reliable communication and sophisticated identity and access management of machines and users will be essential.
Cyber Security: Because increased connectivity and use of standard communications come with Industry 4.0, the need to protect critical industrial systems and manufacturing lines from cyber-security threats will become stronger. Hence, secure, reliable communication and sophisticated identity and access management of machines and users will be essential.
 Additive Manufacturing: The industrial production name for 3-D printing, additive manufacturing is a computer-controlled process that creates three dimensional objects by depositing materials, usually in layers. Using computer aided design (CAD) or 3-D object scanners, additive manufacturing allows for the creation of objects with precise geometric shapes. These are built layer by layer, which is in contrast to traditional manufacturing that often requires machining or other techniques to remove surplus material.
Additive Manufacturing: The industrial production name for 3-D printing, additive manufacturing is a computer-controlled process that creates three dimensional objects by depositing materials, usually in layers. Using computer aided design (CAD) or 3-D object scanners, additive manufacturing allows for the creation of objects with precise geometric shapes. These are built layer by layer, which is in contrast to traditional manufacturing that often requires machining or other techniques to remove surplus material.
 Simulation: In times to come, simulations would be used more extensively in plant operations. These simulations would leverage real-time data to mirror the physical world in a virtual model. This model can include machines, products and humans, thereby allowing operators to test and optimize the machine settings for the next product in line in the virtual world before the desired physical changeover. This will drive down machine setup times and enhance quality.
Simulation: In times to come, simulations would be used more extensively in plant operations. These simulations would leverage real-time data to mirror the physical world in a virtual model. This model can include machines, products and humans, thereby allowing operators to test and optimize the machine settings for the next product in line in the virtual world before the desired physical changeover. This will drive down machine setup times and enhance quality.
 The Cloud: With Industry 4.0, more production-related undertakings will need increased data sharing across sites and company boundaries. As a result, machine data and functionality will increasingly be deployed to the cloud. Even systems that monitor and control processes may become cloud-based.
The Cloud: With Industry 4.0, more production-related undertakings will need increased data sharing across sites and company boundaries. As a result, machine data and functionality will increasingly be deployed to the cloud. Even systems that monitor and control processes may become cloud-based.
 Augmented Reality: Augmented-reality-based systems support services like selecting parts in a warehouse, sending repair instructions over mobile devices, etc. In the future, companies will make greater use of augmented reality to provide workers with real-time information to improve decision-making and work procedures.
Augmented Reality: Augmented-reality-based systems support services like selecting parts in a warehouse, sending repair instructions over mobile devices, etc. In the future, companies will make greater use of augmented reality to provide workers with real-time information to improve decision-making and work procedures.
Digital Manufacturing
What has been the impact of digitalization on industrial production? McKinsey’s Digital Manufacturing Global Expert Survey 2018 reveals two interesting developments taking place in digital manufacturing: organizational commitment and clear progress and stagnation. The survey presents three key findings that characterized the industry’s development in 2018.
It was found that most manufacturing companies consider digital manufacturing a top priority and themselves ahead of the game. On average, 92 percent of respondents reported that they were either on the same level as or ahead of their peers when it came to digital manufacturing. The survey shows that a clear majority of manufacturing companies have already successfully piloted digital solutions. In each area of digital manufacturing – connectivity, intelligence and flexible automation – most of the respondent reported (at least) piloting solutions within their organizations. Across industry sectors and categories, digital manufacturing solutions are adopted consistently. In many cases, companies are piloting multiple digital solutions simultaneously. The global average is eight solutions, but the number varies widely by country. While Indian manufacturers report, on average, piloting more than 10 digital manufacturing technologies at any given time, companies in Japan are, on average, piloting only about four. Also, an analysis of implementation success over time reveals that significantly more companies are reporting successful piloting. Yet while success rates in implementing Digital Manufacturing solutions increases strongly in China, the USA and even Japan, piloting success among German companies has stagnated. Many companies have significant activity underway, but are not yet seeing meaningful bottom-line benefits from production.
The survey also found that for most companies, advancing beyond the pilot phase is still a big challenge. Even when companies report significant number of pilots, most cite significantly less progress in terms of broader rollout. So, while pilots are common, companywide rollout is still rare. In fact, the gap between the piloting and rollout is significantly larger than the gap between perceived relevance and piloting, suggesting that scaling is a bigger hurdle than getting the ball rolling.
An analysis by sector shows that the newer, more technologically advanced areas of the manufacturing sector (for example, industrial automation) are further ahead in the implementation of digital manufacturing than older, more established areas such as paper and packaging.
The results of the Digital Manufacturing Global Expert Survey 2018 clearly indicate that most companies are still struggling to move successfully from the piloting point solutions to delivering sustainable impact at scale. Success stories for capturing sustainable impact at scale are still few.
What Industry 4.0 can do for the wire and cable industry?
Today’s wire and cable industry seems quite ready to engage in the fourth industrial revolution. The industry is changing rapidly. Both consumer and market needs have evolved, and policy pressure and global competition have increased. So, to remain competitive, the industry has to innovate. Innovation can address not only processes, services and products, but also business models, workforce training and education.
Industry 4.0 and Industries in India
In India, automation was not introduced until the early 1990s. It was initially introduced in some of the areas having sensors, Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) loops and stand-alone systems. Automation was first applied to quality control systems, then to process control and finally to the rest of the process. Currently, automation is not just limited to manufacturing processes; it is applied in data management of various operations and functions.
Wire and Cable Industry in India: The Widening Scope for Growth
The buoyant demand for power, light, and communication (data and voice) has provided a fillip to India’s wire and cable industry and electrical equipment business. Industry estimates point at an exciting increase in the share of the organized sector. The Indian wire and cable industry is transitioning away from the unorganized space with small players towards the organized sector consisting of pan-India branded players. The rapid growth of the organized sector has led to the expansion of the size of the market.
The steady rise in consumer spending augurs well for the growth of the wire and cable industry in India. India’s population is estimated to rise to 1.5 bn by 2030 (UN Population Division estimate). The country’s private final consumption expenditure (PFCE), which is a measure of consumption demand, is also rising. The increasing propensity to spend, a steady rise in per capita income and growing urbanization as population rises betoken a bright future for the industry.
According to Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), India’s gross domestic product (GDP) will double over the next 10 years, growing at a rate of 7 per cent per annum. Over this period, the demand for electricity is expected to nearly double. This growth rate will further push the growth of the wire and cable industry in India, which has already hit around Rs 53,000 crore.
The wire and cable market in India, which comprises nearly 40 per cent of the electrical industry, is growing at a CAGR of 15 per cent – thanks to the growth of the power and infrastructure sectors. The recent policy and regulatory initiatives and government schemes like Ujwal Discom Assurance Yojana (UDAY), Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY), Integrated Power Development Scheme (IPDS) and Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana have given the market a major boost. It may be mentioned that under DDUGJY, the government has envisaged the electrification of all villages. Besides, the Indian Railways’ action plan to electrify 38,000 km route in five years from 2017-18 will further whip up demand for wires and cables.
With the outlay of Rs. 2.6 lakh crore announced by the government for the five-year period ending FY2022, the Transmission and Distribution sector is all set to remain in focus for quite some time. There is also a greater focus on high voltage transmission lines along with the government’s aims to provide 24×7 power, which is creating excellent opportunities in the sector. The DISCOMS that have joined the UDAY scheme are expected to improve their T&D infrastructure through renewed investments. The government’s target of generation of 100 GW of solar energy by 2022 and measures like excise duty exemption for ferro silicon magnesium used for manufacturing components of wind-operated electric power generators have also increased the demand for electrical wires and cables.
In addition, the government’s ‘Smart City’ project is expected to promote large-scale growth in infrastructure, telecom, power generation, T&D, engineering and automotive sectors. This is good news for the wire and cable industry because growth of the industry is directly linked to the growth and development taking place in other sectors.
Global investors now consider India as a potential market for high voltage (HV) and extra high voltage (EHV) cables. These investors increase their investments in the Indian cable market through technical collaboration with Indian cable manufacturers for production of EHV cables up to 400 kV. With increasing focus on renewables, the industry is now looking forward to supplying cables for solar and wind power applications in addition to oil and gas, railways and other specialized segments. As per Indian Electrical and Electronics Manufacturers Association (IEEMA), Indian power cable manufacturers have attained maturity in terms of technology for HV cable up to 220 kV and have been found competitive in the global scenario, despite having higher local costs, as well as local taxes and duties being paid on their products.
In addition, electric vehicles (EV) are expected to drive growth for cables and wires firms in a big way. There will be an increased demand for wires and cables when the acceptability of EV picks up. Some amount of wire will also be required to set up EV charging infrastructure.
The Government’s impetus on infrastructure sectors such as power, railways, roads and petrochemicals will in turn spur demand for more power, and hence more power cables. Growing market potential, increased adaption of new technologies by the utilities, growing importance of services that may be linked to digital technologies have widened the scope for the growth of the wire and cable industry in India.
The wire and cable industry expects a spurt in manufacturing activity and capacity expansion in sectors like steel, cement, pharma, etc. Also, in line with Supreme Court’s directive to reduce emissions as per BS-VI norms, petrochemical companies are expected to invest in plant modernization and expansion. This move will further stimulate the demand for cables.
Industry 4.0 – A Smart Solution
The highly attractive market for wires and cables in India has grown exponentially and is bound to expand in future. Wire and cable companies, therefore, need to be prepared to respond quickly to changing levels of demand. They need to find ways of how to improve effectiveness of management, how to produce more, how to produce faster and how to improve the way they work with customers and other partners, with cooperation becoming even closer in future. In this scenario, one of the solutions is digital transformation.
This transformation entails development of new technologies and processes that can be used to increase productivity. Adoption of Industry 4.0, however, does not mean that a company needs to invest in new equipment to raise its productivity. A company can produce more with the same equipment by employing digitization. For example, the most widespread management system at the shop-floor is Microsoft Excel, which is not part of Industry 4.0. It is far from digitization, but digitization can make it more effective. A company can improve its management system and adjust its processes based on the Industry 4.0 ideology. In addition, a company can make R&D faster with Industry 4.0. Also, because of complete linking and communication on all levels of the production process considerable amelioration with regard to productivity and flexibility may result. Besides, adoption of Industry 4.0 can synchronize equipment and workers in a better way. It can, to put it briefly, turn a factory into a “smart factory”.
Digitization is all about scale customization; it makes manufacturing much more productive and flexible. Wire and cable companies must turn to Industry 4.0 for more productivity, output and growth and for production of better and smarter products. Industry 4.0 is surely the need of the hour.
Eurolls’ New Technology
Eurolls has adopted Digital Integration, Industry 4.0 and various other automation systems to enhance and simplify its manufacturing process to the benefit of the final end user. This continuous investment in Research and Development provides Eurolls with increased flexibility and higher quality standards and significantly improves its manufacturing efficiencies.
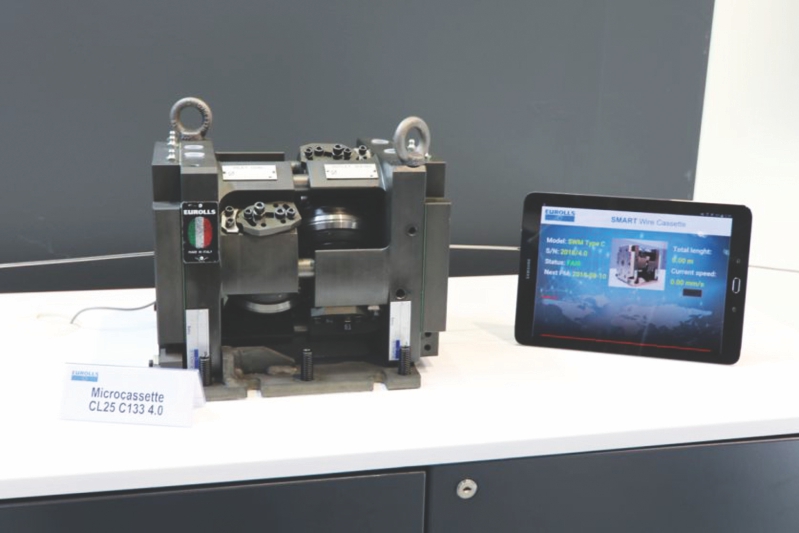
During last month’s exhibition in Düsseldorf, Germany, Eurolls introduced several new developments. Exhibited was its latest innovation, the prototype SMART CASSETTE 4.0. This new SMART CASSETTE, launched in partnership with Udine University, features an enhanced heart with digital sensors that are able to monitor and analyze effective production performances. Eurolls SMART CASSETTE 4.0 is remotely accessible by tablet and/or smartphone and sends users a notification when it detects anomalous values in the production process (i.e. temperatures, vibrations, wire dimensions, etc.). The system is fully compatible with a 4.0 data logging system to maximize the benefits in terms of production information.
Thanks to this new technology, it will also be possible to track the real working time of each cassette, providing users with the actual working life of their rolls (in tonnage), which is one of the most frequently asked questions by the company’s customers. This newest modern innovation has been designed to give customers a preventative maintenance solution, as traditionally, the cold rolling cassettes used merely a corrective maintenance approach. This development is perfectly integrated with Eurolls Rolling Machinery, with HMI, that are enhanced to receive the data coming from the cassettes for proper and total system management.
Giulio Properzi, CEO & President, Continuus Properzi; Giovanni Pirovano, Manager, Electrical & Automation; and Alberto Ghisetti, Sales Director, talk about Industry 4.0 and the wire and cable industry in interviews given to Wire & Cable India.
WCI: What is Industry 4.0 and what can it do for the wire & cable industry?

Giovanni Pirovano: The term Industry 4.0 identifies the fourth industrial revolution; in essence, the evolution of factorie introducing the latest information and automation technologies into production processes to reach a high degree of digitization and data exchange capability through the Internet as a means to improve productivity, efficiency, and reactivity to new market demands. This improvement is pursued by employing large amounts of data collected by sensors and actuators of newly implemented functionalities designed to increase machines’ interconnection and data transparency while improving features for technical assistance and decentralized decisions.
Like other manufacturing sectors, the wire and cable industry, in practice, can benefit from this revolution by using this data to monitor and measure process performance in such a way to facilitate more effective and timely decisions by the managers. A second step is the identification, and subsequent adoption, among the wide set of I4.0 technologies offered by the market, of those technologies which offer the greatest potential benefit(s) for the concerned business sector. Examples of such technologies are Industrial Internet of Things, Collaborative Robots, Augmented Reality, Twin Digital, Cloud Computing, Big Data Analytics, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Artificial Intelligence. The challenge lies in understanding which technology has the potential today to become a so-called “Exponential Technology” in the wire and cable industry in the future and therefore represents a real opportunity for investing in its development.
WCI: Have you implemented Industry 4.0 in your company? If you have, then could you tell us a little bit about it? If you haven’t, then are you planning to implement it?
Giovanni Pirovano: We have internally converted and replaced the majority of machine tools in our workshop with Industry 4.0 machines interconnected with our IT system and this process is continuously evolving. Regarding the design and production of machinery, Continuus-Properzi has always been attentive to innovations and new solutions as opportunities to be seized in order to raise the quality of the plants, to consolidate our experience and knowledge, and to make these assets available to our users in relation to their specific needs. Consistent with this approach, we have outlined a “road map” to offer support to users who find themselves having to choose between purchasing new plants or modernizing the existing ones.
As a first step, automation architecture designed to provide a modular infrastructure and open to future development of new functions was studied and then gradually introduced.
Subsequently, we introduced functionalities such as:
- Remote Technical Assistance on plants’ automation from our company headquarters through the Internet,
- Provision for making it possible for the users to access, though their mobile devices, information of interest taken from HMI and SCADA pages of the plant,
- Elaboration of more specific indicators, meaningful of process status and performances, grouped by managers’ roles (i.e. production, maintenance, etc.), to better support their decisional processes, and
- Sharing of SCADA collected data with the user’s IT system through a dedicated open database.
Further improvements of the above functionalities are ongoing, as well as studies of new ones, for an ever-deeper knowledge of the production processes and more advanced decision-making models to support the users.
WCI: Is Industry 4.0 technology affordable enough for developing countries?

Alberto Ghisetti: The Industry 4.0 technology is more than affordable for developing countries; some solutions are even designed to reduce the operational and maintenance costs with a very limited investment. For example, if we consider the remote assistance service, Continuus-Properzi’s experts can solve problems in real time drastically reducing equipment downtime and the costs of the technical assistance intervention itself.
WCI: Exponential Technologies are a reality and the real challenge is to identify how to implement them in our industry in a way that adds real value. Should the wire and cable industry in India go for exponential technologies? Are the wire and cable companies in India ready to implement Industry 4.0?
Alberto Ghisetti: Continuus-Properzi is convinced that the wire and cable companies in India are ready to implement Industry 4.0 in new projects and existing plants. We emphasize that it is important to select the right elements of this new technology that can add value and, since we are the most experienced company in this sector, we are available to support our customers in this activity.
WCI: The process of automation and digitization has begun in the wire and cable industry, but the industry is yet to take this whole experience to a new level, which means beyond the process. Do you agree with this observation? Please elaborate.
Alberto Ghisetti: We agree that the automation and digitalization in the wire and cable industry began several years ago; however, we have already developed technological solutions that are able to provide some selected information to higher automation levels for several purposes, not strictly linked to the process. For this reason we believe that the time is ripe for the wire and cable industry to deal with this new industrial revolution.
WCI: Experts say that Industry 4.0 applications will disrupt classical customer service models. Do you endorse this view?

Giulio Properzi: Customer service has many different appearances, but Industry 4.0 does not change drastically what is already a standard way of remote service or on-site service. Only the number of parameters is greater and they will be further multiplied by the new technologies. The response time and the ease of solving some particular problems will be advantages that can be obtained through Industry 4.0 which will offer an extra service, without replacing the classic customer service.
WCI: Don’t you think automation will increase joblessness, especially in developing economies?
Giulio Properzi: Not completely. Automation and robotics will certainly eliminate some jobs but at the same time will create a good number of new, higher-paying jobs. In addition, the total demand of products and services will surely increase thereby creating new jobs. We foresee some possible problems only in certain regional or localized situations.
“Of course, ignoring innovation is no option; it’s a dead-end street. Wire and cable companies in India should plan for the future and invest in a technology platform that enables them for innovation now and in the future,” says Albert Groothedde, CEO, InnoVites.

Wire & Cable India: What is Industry 4.0 and what can it do for the wire & cable industry?
Albert Groothedde: When it comes to Industry 4.0, InnoVites’ focus is on smart cable factory. We provide IT solutions that help our customers to convert their factory into a smart cable factory. A smart cable factory thrives in a continuous changing environment, using the massive amount of information (Big Data) that is being collected. The InnoVites CableSuite integrates business processes to allow engineers, the sales teams and the production team to work together in providing the best customer solution with the shortest lead times. The short feedback cycles result in continuous improvements, which boost the business performance.
WCI: Have you implemented Industry 4.0 in your company? If you have, then could you tell us a little bit about it? If you haven’t, then are you planning to implement it?
AG: We provide our customers with the technology that helps them to become a smart cable factory.
WCI: Is Industry 4.0 technology affordable enough for developing countries?
AG: Sure, the benefits are significant in higher quality, faster customer responses and increased sales. So there is a return on investment for Industry 4.0-related projects.
WCI: Exponential Technologies are a reality and the real challenge is to identify how to implement them in our industry in a way that adds real value. Should the wire and cable industry in India go for exponential technologies? Are the wire and cable companies in India ready to implement Industry 4.0?
AG: Of course, ignoring innovation is no option; it’s a dead-end street. Wire and cable companies in India should plan for the future and invest in a technology platform that enables them for innovation now and in the future.
WCI: The process of automation and digitization has begun in the wire and cable industry, but the industry is yet to take this whole experience to a new level, which means beyond the process. Do you agree with this observation? Please elaborate.
AG: The information technology that supports this process has become affordable. The level of customer expectations is also rising, so it’s important for the industry to embark on these initiatives to avoid to be left behind.
WCI: Experts say that Industry 4.0 applications will disrupt classical customer service models. Do you endorse this view?
AG: This may indeed be the case. However the wire and cable industry has never been a front runner in introducing new business models. I expect that new customer service models will mature first in other industries before they are adopted in the wire and cable industry.
WCI: Don’t you think automation will increase joblessness, especially in developing economies?
AG: This is the classical debate about automation. I believe automation will indeed increase productivity in the manufacturing industry. However, there will be a need for new jobs to support the process of automation and innovation as well. So, the net result will be positive for a country as a whole.