In order to bring reliable power supply in India, ABB has a range of digital solutions for smarter grid system. ABB India will also deliver one of India’s first fully operational digital substations for the nation’s largest IT Park in Kerala.
August 16, 2017
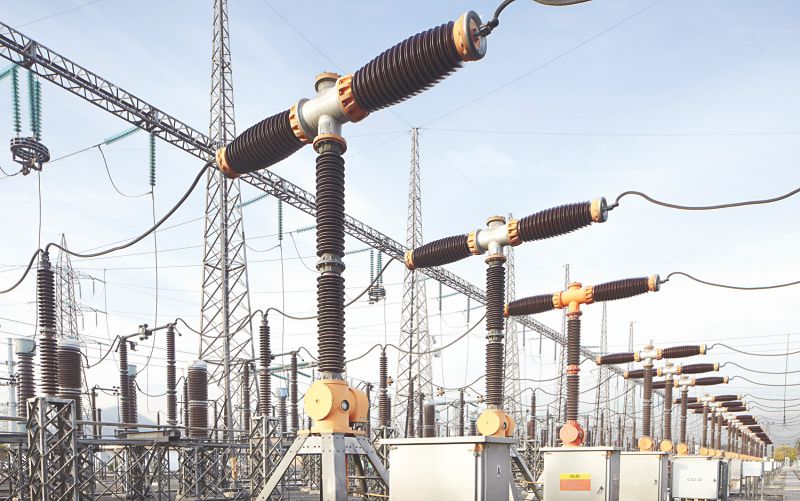

ABB India will upgrade 20 substations in Himachal Pradesh – the foothills of the Himalayas. The substations will be equipped with the latest control and protection technology to enable future digitalization. The order, placed by the local state utility, Himachal Pradesh Electricity Board Limited (HPSEBL), supports India’s Smart Grid Vision and the government’s ambition of providing reliable power to the country’s most remote regions.
ABB India will deploy its Relion® electronic relays for the protection, control, measurement and supervision of power systems at all twenty substations. Six of the substations will also be equipped with ABB’s state-of-the-art MicroSCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system, which will ensure the optimized control and reliable operation of the substation through seamless integration and connectivity between different devices and systems. Both products are a part of the company’s ABB Ability™, its industry-leading portfolio of digital solutions, which help turn data insights into actionable intelligence.
A digital substation is a key component to enabling a smarter grid. Digital communications via fiber optic cables replace traditional copper connections using analog signals, increasing safety, flexibility and availability, while reducing cost, risk and environmental impact. Built on the international standard IEC 61850, ABB’s world-leading digital substations bring increased reliability, interoperability and real-time performance.
ABB India will also deliver one of India’s first fully operational digital substations for the nation’s largest IT Park in Kerala. ABB has been integral in the development of India’s power infrastructure across challenging terrains. For example, ABB recently commissioned the Khandukhal substation in the mountainous state of Uttarakhand, which evacuates power generated from the rivers of the northern state and integrates it with the national grid.